Vandaag hebben we een bijzonder informatief onderwerp voor je in petto: de follikel! Misschien heb je er wel eens van gehoord in een biologieklasje op school of misschien is dit de eerste keer dat het woord je oren bereikt. Hoe dan ook, we gaan je alles vertellen wat je moet weten over deze fascinerende kleine structuren in het lichaam. Van hun rol in de voortplantingscyclus tot hoe je ze kunt ondersteunen voor een optimale gezondheid, we gaan geen detail onbesproken laten.
Wat is een follikel?
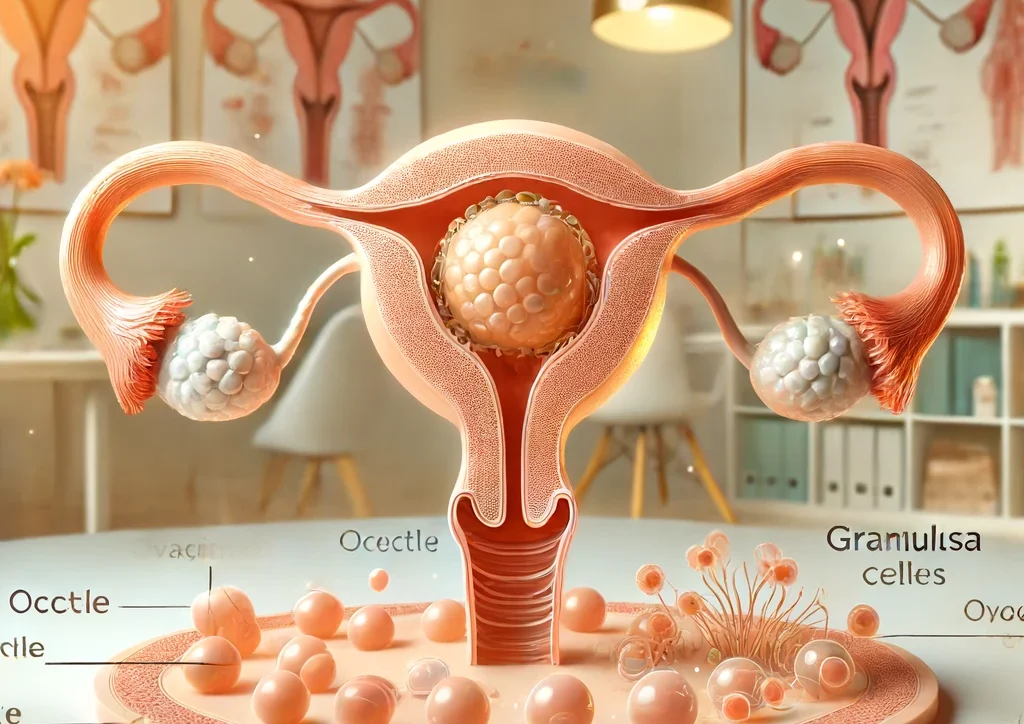
Een follikel is in feite een kleine, met vloeistof gevulde zak die een belangrijk onderdeel is van je voortplantingssysteem. Elke maand rijpt in je eierstokken een follikel die een eicel bevat. Dit kleine blaasje zorgt niet alleen voor de ontwikkeling van je eicellen maar produceert ook hormonen zoals oestrogeen en progesteron, essentieel voor het reguleren van je menstruatiecyclus. Kortom, zonder deze machtige mini-structuren zou voortplanting een stuk ingewikkelder zijn.
Wil je weten wanneer je follikels hun werk doen? Eerste, ze groeien en rijpen tijdens je menstruatiecyclus. Vervolgens, als ze klaar zijn, barst een van de meest volwassen follikels open en komt je eicel vrij. Deze gebeurtenis, bekend als ovulatie, is cruciaal voor bevruchting. Een gezonde follikel kan oestrogeen en progesteron produceren, wat bijdraagt aan een stabiele menstruatiecyclus. Het onderhouden van gezonde follikels is essentieel voor je vruchtbaarheid en algemene gezondheid.
-
- Follikelgroei bevorderen door een gezonde levensstijl
-
- Regelmatige medische controles voor follikelgezondheid
-
- Symptomen zoals buikpijn of onregelmatige menstruatie kunnen op follikelproblemen wijzen
| Kenmerk | Functie |
|---|---|
| Bevat eicel | Zorgt voor bevruchting |
| Produceert hormonen | Reguleert menstruatiecyclus |
Hoe groeit een follikel?
Het folliculaire groeiproces is zowel fascinerend als complex! Een follikel begint zijn levenscyclus als een kleine holte in de eierstok. Deze holte bevat een eicel en wordt omringd door granulosa- en thecacellen. Deze cellen spelen een cruciale rol bij de rijping van de eicel en de productie van hormonen zoals oestrogeen. Gedurende de eerste fase van de menstruatiecyclus, wordt de groei van de follikel gestimuleerd door het follikelstimulerend hormoon (FSH). Naarmate de follikel groeit, produceert hij meer oestrogeen en bereidt hij de eicel voor op de ovulatie.
Halverwege de cyclus gebeurt er iets indrukwekkends: de dominante follikel, die alle andere voorbij is gestreefd, barst open. Hierdoor komt de rijpe eicel vrij, klaar voor een mogelijke bevruchting. Ondertussen veranderen de granulosa- en thecacellen van de voormalige follikel in het corpus luteum, een belangrijke structuur die progesteron produceert om de baarmoederwand voor te bereiden op een eventuele zwangerschap. Fascinerend, toch?
| Fase | Belangrijkste Gebeurtenissen |
|---|---|
| Follikelgroei | Stimulatie door FSH, toename van oestrogeen |
| Ovulatie | Barsten van de dominante follikel, vrijlating eicel |
| Corpus luteum | Productie van progesteron, voorbereiding op zwangerschap |
Follikels en je menstruatiecyclus
-
- Reguleren van de menstruatiecyclus
-
- Ondersteunen van de baarmoederwand
-
- Verbeteren van stemming en energie
In het volgende overzicht zie je de veranderingen van follikels tijdens de cyclus:
| Fase | Follikels |
|---|---|
| Folliculaire fase | Groei en rijping |
| Ovulatie | Eicel vrijgegeven |
| Luteale fase | Geel lichaam vormt |
Bij Verloskundigen PuurBegin helpen we je graag om je cyclus beter te begrijpen. Neem gerust contact op voor meer informatie!
De eisprong
Tijdens de eisprong barst een rijpe eicel uit de follikel en begint haar reis door de eileider, op zoek naar een mogelijke bevruchting. Dit proces vindt meestal plaats rond de veertiende dag van je menstruatiecyclus. Het hormoon luteïniserend hormoon (LH) speelt hierbij een cruciale rol, want het stimuleert de follikel om te groeien totdat deze klaar is om te ovuleren. Hoewel dit elke maand gebeurt, kan de precieze timing variëren door verschillende factoren zoals stress, dieet en lichaamsgewicht. Bovendien, zodra de follikel barst, zal het resterende deel zich omvormen tot het corpus luteum, welke progesteron aanmaakt om een mogelijke zwangerschap te ondersteunen.
Sommige vrouwen ervaren symptomen tijdens de ovulatie, zoals lichte krampen of een verhoogd libido. Deze symptomen kunnen nuttig zijn als je probeert zwanger te raken of juist zwangerschap wilt voorkomen. Hier zijn een paar tekenen van de ovulatie:
-
- Verandering in baarmoederhalsslijm
-
- Verhoogde lichaamstemperatuur
| Symptoom | Beschrijving |
|---|---|
| Baarmoederhalsslijm | Helder en rekbaar, zoals eiwit |
| Lichaamstemperatuur | Stijging van 0.5 tot 1 graad |
| Ovulatiepijn | Lichte krampen aan één zijde |
Het gele lichaam
Het gele lichaam, ook bekend als het corpus luteum, speelt een cruciale rol in de menstruatiecyclus. Zodra de eisprong plaatsvindt, transformeert de lege follikel in dit tijdelijke endocriene orgaan. Bijzonder is dat het direct begint met de productie van belangrijke hormonen zoals progesteron en oestrogeen. Deze hormonen zijn essentieel voor het voorbereiden van de baarmoeder op een mogelijke zwangerschap. Dit delicate, maar krachtige proces zorgt ervoor dat de voering van de baarmoeder dikker wordt, waardoor het embryo kan innestelen. Zonder zou dit hele proces ernstig worden verstoord.
Wat er gebeurt met verschilt afhankelijk van of er al dan niet een zwangerschap optreedt. Als er geen bevruchting plaatsvindt, zal het corpus luteum na ongeveer 14 dagen afbreken, wat leidt tot een daling van progesteron- en oestrogeenniveaus en uiteindelijk tot de menstruatie. Bij een zwangerschap blijft actief, produceert het hormonen en ondersteunt het de vroege fasen van de zwangerschap totdat de placenta deze taak overneemt. Dit magische mechanisme toont de fascinerende precisie van ons lichaam.
Opmerkelijke Feiten over:
-
- Tijdsgevoelig: functioneert gewoonlijk slechts ongeveer twee weken als er geen zwangerschap optreedt.
-
- Hormoonproducent: Het corpus luteum produceert dagelijks aanzienlijke hoeveelheden progesteron.
-
- Natuurlijk Verval: In de laatste fase van zijn bestaan krimpt en stopt het met hormoonproductie, wat de menstruatiecyclus beëindigt.
Korte Beschrijving en Functie
| Kernpunt | Uitleg |
|---|---|
| Gele Lichaam | Een tijdelijke structuur in de eierstok |
| Hormoonproductie | Produceert progesteron en oestrogeen |
| Duur | Ongeveer 14 dagen zonder zwangerschap |
Conclusie
Tot zover alles wat je moet weten over follikels! We hopen dat dit artikel je een helder inzicht heeft gegeven in de fascinerende wereld van de follikels en hun belangrijke rol in je gezondheid. Of je nu benieuwd was naar hoe je cyclus werkt, of gewoon wat dieper in de materie wilde duiken, we zijn blij dat je de tijd hebt genomen om dit te lezen.
Heb je nog vragen of wil je meer weten over dit onderwerp? Aarzel dan niet om contact met ons op te nemen. Bij Verloskundigen PuurBegin staan we altijd voor je klaar om je te informeren en ondersteunen, wat je vraag ook is. Ons doel is om je te helpen een goed begrip te krijgen van je lichaam en gezondheid, zodat je met vertrouwen je keuzes kunt maken.
Blijf op de hoogte!
Volg ons op social media voor het laatste nieuws en een kijkje achter de schermen bij Verloskundigen PuurBegin in Kampen.
Ontdek de dagelijkse avonturen van onze verloskundigen, waardevolle tips voor aanstaande ouders en inspirerende verhalen uit de praktijk.
Klik op de onderstaande knoppen en blijf verbonden met ons hartverwarmende team!
 |
 |
Hartelijke groet,
Verloskundigen PuurBegin
Adres: Orkestlaan 148, 8265RC Kampen
Telefoon: 085 40 19 095