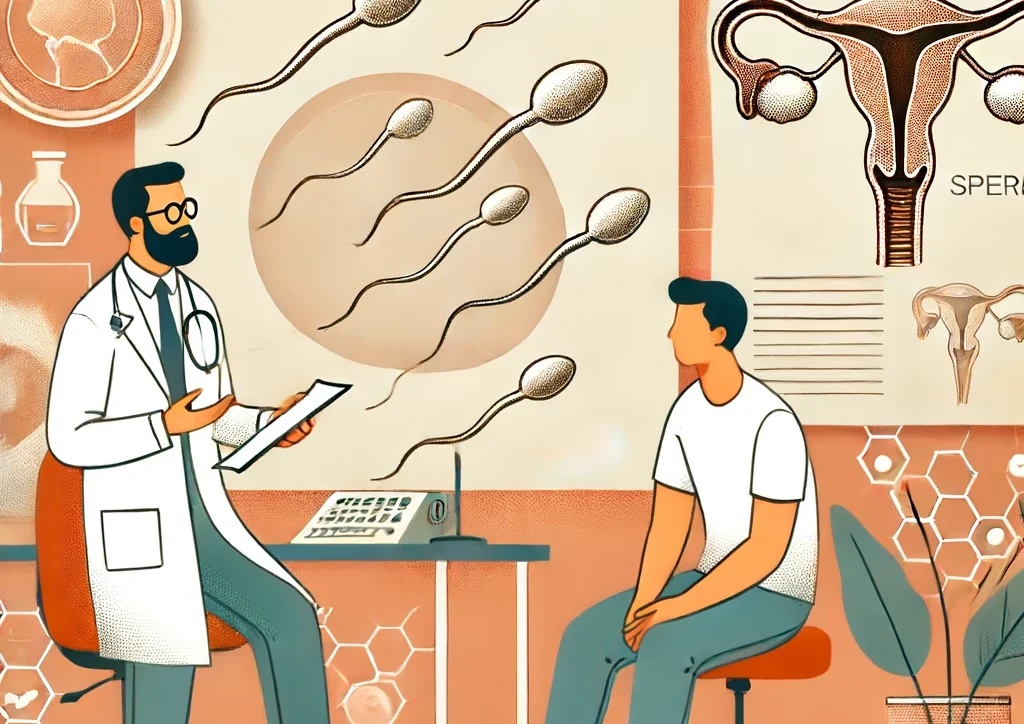
Vandaag gaan we het hebben over een fascinerend onderwerp dat vaak over het hoofd wordt gezien: de mannelijke zaadcel. In ons artikel ”Sperma Ontrafeld” duiken we diep in de wereld van het sperma. We nemen je mee op een informatieve maar toegankelijke reis vol met interessante weetjes en wetenschappelijke inzichten. Van de magische ontmoeting met de eicel tot hoe leefstijlkeuzes de gezondheid van zaadcellen beïnvloeden, we laten geen aspect onbesproken.
Wat is sperma?
-
- Fructose voor energie
-
- Proteïnen voor bescherming
-
- enzymen voor ondersteuning
Daarnaast bevatten de vloeistoffen ook hormonen zoals prostaglandinen die helpen bij de samentrekking van het vrouwelijke voortplantingsstelsel, wat de zaadcellen weer een extra zetje geeft. Niet te vergeten is de pH-waarde, die licht alkalisch is, wat helpt om de zure omgeving in de vagina te neutraliseren.
| Component | Functie |
|---|---|
| Fructose | Energiebron |
| Prostaglandinen | Hormonale ondersteuning |
| pH-buffering | Zuren neutraliseren |
De mannelijke zaadcel
De zaadcel ofwel spermacel, is een meesterwerk van de natuur, ontworpen voor één enkel doel: het bevruchten van een eicel. Wat de zaadcel zo bijzonder maakt, is niet alleen zijn grootte, maar ook zijn compenserende anatomie. Een doorsnee zaadcel meet slechts circa 0,006 millimeter, maar beschikt over een ingenieuze opbouw. De spermacel bestaat uit drie hoofdcomponenten:

-
- Hoofd: Bevat de kern met 23 chromosomen, nodig voor de bevruchting.
-
- Middenstuk: Bevat mitochondriën die energie leveren voor beweging.
-
- Staart: Zorgt voor voortstuwing door in een wavelachtige beweging te bewegen.
| Onderdeel | Functie |
|---|---|
| Hoofd | Chromosomenoverdracht |
| Middenstuk | Energieproductie |
| Staart | Voortbeweging |
Interessant is dat een zaadcel in zijn korte levensduur een ware marathon aflegt. Vanaf het moment van ejaculatie tot aan de bevruchting reist hij ongeveer 15 tot 20 centimeter door de vrouwelijke voortplantingsorganen. Onderweg moet hij tal van obstakels overwinnen, zoals zure omgevingen en fysieke barrières. Toegegeven, slechts een fractie van de miljoenen spermacellen bereikt de eicel, maar diegenen die het halen, zijn werkelijk de fitste van de fitste. Dat maakt het proces van conceptie niet alleen fascinerend maar ook een ware krachttoer van de natuur.
Samenstelling zaad
-
- Prostaatvocht
-
- Vloeistof uit de zaadblaasjes
-
- Vloeistof van de Cowperse klieren
Deze vloeistoffen zijn essentieel omdat ze de zaadcellen beschermen en voeden, waardoor de kans op succesvolle bevruchting aanzienlijk wordt vergroot.
De route van sperma bij een zaadlozing
Tijdens een zaadlozing begint de reis van het sperma in de teelballen (testikels), waar miljoenen spermacellen worden geproduceerd. Vanuit daar bewegen de zaadcellen naar de bijballen (epididymis), waar ze worden opgeslagen en rijpen. Vervolgens gaan de zaadcellen door de zaadleiders (vas deferens), een smal, buisvormig kanaal dat naar de prostaat leidt. De weg waarop ze reizen kan verwarrend zijn, maar elke stap is cruciaal voor bevruchting.
Daarna voegen de zaadblaasjes (seminal vesicles) en de prostaat klier zich bij deze reis. De zaadblaasjes voegen een vloeistof toe die rijk is aan suiker, die energie biedt aan de spermacellen. Wanneer het sperma door de prostaat gaat, wordt er nog meer vloeistof toegevoegd om het sperma te laten zwemmen. Dit alles komt uit in de urethra bij de penis en tijdens een orgasme vindt de spectaculaire climax plaats wanneer het sperma de eikel verlaat. Hier is een overzicht:
| Stap | Beschrijving |
|---|---|
| 1 | Productie in de teelballen |
| 2 | Opslag in de bijballen |
| 3 | Transport door de zaadleiders |
| 4 | Menging met vocht van zaadblaasjes en prostaat |
| 5 | Uiteindelijke uitstoot via de urethra |
Bij elke stap krijgen de zaadcellen precies wat ze nodig hebben om hun ultieme doel te bereiken: de eicel bevruchten. Ondanks de verschillende stadia is het een zorgvuldig gecoördineerd proces waarbij elke fase onmisbaar is.
De tocht naar de eicel
De reis van zaadcellen begint zodra ze de baarmoederhals bereiken. Ongeveer 250 miljoen zaadcellen vertrekken op deze uitdagende expeditie, maar slechts een handjevol zal daadwerkelijk de eicel bereiken. Zodra ze de baarmoederhals hebben gepasseerd, komen ze in de baarmoeder terecht, waar een ware survivaltocht begint. Binnen enkele uren zijn de meeste zaadcellen al afgebroken of afgewend. Alleen de sterksten en snelsten overleven.
Eenmaal in de eileider aangekomen, staan de zaadcellen voor hun laatste hindernis. Hier zijn slechts enkele duizenden van hen nog in leven. De omgeving is hier extra vijandig, en een reeks biologische obstakels wacht hen op. De gelukkigen die dit stadium overleven, kunnen eindelijk proberen de eicel te penetreren. Belangrijke factoren die deze reis beïnvloeden zijn:
-
- Snelheid – De snelste zaadcellen hebben het meeste succes.
-
- Richting – Zonder een goed gevoel van richting, raken zaadcellen verdwaald.
-
- Biologische factoren – Alleen de gezondste en sterkste zaadcellen kunnen door de schil van de eicel dringen.
De strijd om bevruchting
-
- Snelheid: De spermacel moet zich snel en efficiënt voortbewegen om de eicel te bereiken.
-
- Uithoudingsvermogen: Alleen de sterkste zaadcellen overleven de lange reis naar de eicel.
-
- Richting: Zaadcellen moeten de juiste weg vinden naar de eileider.
| Eigenschap | Belang |
|---|---|
| Snelheid | Hoog |
| Uithoudingsvermogen | Hoog |
| Richting | Essentieel |
Levensduur van sperma
Wanneer je je afvraagt hoe lang sperma daadwerkelijk leeft, is het belangrijk om te weten dat de levensduur sterk varieert afhankelijk van de omstandigheden. In de baarmoeder en eileiders kunnen zaadcellen tot wel vijf dagen overleven, vooral in een gunstige omgeving. Dit biedt een ruime “conceptie-vriendelijke” periode, wat betekent dat je zwangerschapskansen groter zijn indien seks plaatsvindt vlak voor of tijdens de eisprong.
Buiten het lichaam daarentegen, bijvoorbeeld op huid of kleding, leeft sperma meestal niet langer dan een paar minuten. Dit komt omdat het vocht snel verdampt en de cellen uitdrogen. Factoren die de levensduur beïnvloeden zijn onder andere:
-
- pH-waarde van de omgeving
-
- Aanwezigheid van cervicale slijm
-
- Temperatuur
Kortom, onder perfecte omstandigheden kunnen zaadcellen verrassend lang overleven, maar deze situatie is buiten het lichaam veel minder gunstig.
| Omgeving | Levensduur |
|---|---|
| Binnen de baarmoeder | Tot maximaal 5 dagen |
| Op huid of kleding | Enkele minuten |
Temperatuur van de ballen voor de aanmaak van sperma
De temperatuur van de teelballen speelt een cruciale rol in de productie van sperma. Om optimaal sperma te produceren, moeten de teelballen een temperatuur hebben die ongeveer 2 tot 3 graden lager is dan de lichaamstemperatuur. Dit subtiele verschil is essentieel voor de ontwikkeling en levensvatbaarheid van de zaadcellen. Te hoge temperaturen kunnen de spermatogenese (het proces van zaadcelvorming) aanzienlijk verstoren. Testikels die bijvoorbeeld tijdens sportactiviteiten of door strakke kleding oververhit raken, kunnen tijdelijk de kwaliteit en kwantiteit van zaadcellen verminderen. Bovendien kan langdurige blootstelling aan hoge temperaturen leiden tot blijvende schade.
Er zijn verschillende manieren om te zorgen voor een optimale temperatuur voor de teelballen:
-
- Draag loszittende kleding zoals boxershorts in plaats van strakke slips.
-
- Vermijd hete baden en saunabezoeken.
-
- Zorg voor een gezond dieet en blijf gehydrateerd.
Als het nog niet genoeg duidelijk is hoe belangrijk dit is, laten we een vergelijkend overzicht zien:
| Factor | Positief Effect | Negatief Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Losse Kleding | Optimale Temperatuur | Nee |
| Hete Baden | Nee | Oververhitting |
| Goede Hydratatie | Verbeterde Spermakwaliteit | Nee |
Spermakwaliteit verbeteren
Een aanzienlijke verbetering van de kwaliteit van je zaadcellen kan worden bereikt door een aantal eenvoudige aanpassingen in je dagelijkse leven. Voeding speelt hierbij een cruciale rol. Probeer een dieet te volgen dat rijk is aan antioxidanten, omega-3 vetzuren en foliumzuur. Voeg voedingsmiddelen zoals vis, noten, zaden, bladgroenten en fruit toe aan je maaltijden. Daarnaast is het belangrijk om de consumptie van alcohol en cafeïne te verminderen, omdat deze de spermakwaliteit nadelig kunnen beïnvloeden. Drink voldoende water om gehydrateerd te blijven.
Een andere effectieve manier om de spermakwaliteit te verbeteren is door regelmatige lichaamsbeweging. Beweeg dagelijks en zorg voor voldoende nachtrust. Stressmanagement is ook essentieel, omdat te veel stress kan leiden tot hormonale onevenwichtigheden die de spermaconcentratie en -beweeglijkheid kunnen schaden. Probeer ontspanningstechnieken zoals meditatie of yoga. Tot slot, vermijd overmatige hitte, zoals hete baden of sauna’s, omdat warmte de zaadproductie negatief beïnvloedt.
| Voedingsmiddel | Voordeel |
|---|---|
| Vis | Rijk aan Omega-3 |
| Fruit | Bevat antioxidanten |
| Bladgroenten | Hoge foliumzuurlevels |
Samenvatting
Dus, daar heb je het: de fascinerende wereld van de mannelijke zaadcel, ontrafeld en tot in detail uitgelegd. We hopen dat je nu iets meer begrijpt van wat er allemaal komt kijken bij de reis van een spermacel van oorsprong tot doel. Bij Verloskundigen PuurBegin vinden we het belangrijk dat je goed geïnformeerd bent over je lichaam en alle bijzondere processen die erbij horen. Want kennis geeft kracht, toch?
Mocht je vragen hebben over kinderwens, vruchtbaarheid of gewoon nieuwsgierig zijn naar meer, aarzel dan niet om contact met ons op te nemen. Ons team van deskundige verloskundigen staat altijd klaar om je te helpen en te begeleiden.
Blijf nieuwsgierig en zorg goed voor jezelf!
Blijf op de hoogte!
Volg ons op social media voor het laatste nieuws en een kijkje achter de schermen bij Verloskundigen PuurBegin in Kampen.
Ontdek de dagelijkse avonturen van onze verloskundigen, waardevolle tips voor aanstaande ouders en inspirerende verhalen uit de praktijk.
Klik op de onderstaande knoppen en blijf verbonden met ons hartverwarmende team!
 |
 |
Hartelijke groet,
Verloskundigen PuurBegin
Adres: Orkestlaan 148, 8265RC Kampen
Telefoon: 085 40 19 095